Identity and Access Management
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/iam/index.html
FAQs: https://aws.amazon.com/iam/faqs/
Security best practices in IAM - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/best-practices.html
Enable IAM Access Analyzer
See some use cases at Security best practices in IAM
It can generate policies - see below
Note that this is a paid service.
A vault for securely storing and accessing AWS credentials in development environments - https://github.com/99designs/aws-vault
Cloudsplaining is an AWS IAM Security Assessment tool that identifies violations of least privilege and generates a risk-prioritized report - https://github.com/salesforce/cloudsplaining
A tool for quickly evaluating IAM permissions in AWS - https://github.com/nccgroup/PMapper
Refining permissions in AWS using last accessed information - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/access_policies_access-advisor.html
AWS Vault - https://github.com/99designs/aws-vault - Stores IAM credentials in your operating system's secure keystore
IAM is a global service. Notice you cannot select any region at the top-right dropdown at the console. Any user, group, role etc. can be used on all regions, all around the world.
Summary
- User: an individual, system or application running outside of AWS requiring access to AWS services.
- Group: collection of users with the same permissions. A user can be in many groups.
- Role: set of permissions. Used to authenticate AWS entities such as EC2 instances.
- Policy: JSON file. Permissions assigned to a user, group or role.
- Principal: user, account, service, or other entity that is allowed or denied access to a resource. Principals are authenticated IAM entities. Can be (source):
- AWS account and root user
- IAM roles
- Role sessions
- IAM users
- Federated user sessions
- AWS services
- All principals
- Resource: the IAM service stores these resources. You can add, edit, and remove them from the Console.
- IAM user
- IAM group
- IAM role
- Permission policy
- Identity-provider object
- Entity: IAM resources that AWS uses for authentication. A type of identity that represents a human user or programmatic workload that can be authenticated and then authorized to perform actions in AWS accounts. Specify the entity as a Principal in a resource-based policy.
- IAM users
- IAM roles
- Identity: the IAM resource that's authorized in policies to perform actions and to access resources. Can be associated with one or more policies, which determine what actions an identity is authorized to perform, on which AWS resources, and under what conditions.
- IAM root user
- IAM users
- IAM groups
- IAM roles
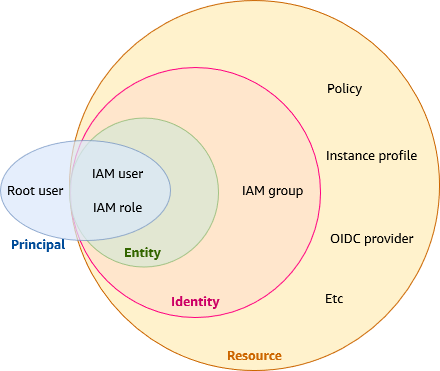
IAM Identities - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id.html
Nice summary - https://blog.awsfundamentals.com/aws-iam-roles-terms-concepts-and-examples
Cheatsheet - https://digitalcloud.training/aws-iam/
User
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_users.html
A human user or workload who uses the IAM user to interact with AWS resources.
Users have no permissions by default, thus they can't do anything. You give them permissions using groups and policies.
Each user has a username (Account name), used to log in.
Authentication options:
- Web console: username and password + optionally MFA.
- To log in at the console use the URL
https://$accountId.signin.aws.amazon.com/consoleorhttps://$accountAlias.signin.aws.amazon.com/console. (Useaws sts get-caller-identityto get the account ID.)
- To log in at the console use the URL
- CLI, SDK & API: access key ID and secret access key. You can additionally require MFA.
- Only a user can have access keys (not a group nor role).
- Best practice: use roles for applications that run on EC2 instances or lambda functions. See Require workloads to use temporary credentials with IAM roles to access AWS
- Access keys are long term credentials. You can use the Security Token Service (STS) to generate temporary credentials, eg with
assume-roleandget-session-token. See Temporary security credentials in IAM.
You should set up a unique IAM user for every person who needs access to the AWS account, and grant access only to the resources each person needs, following the least-privilege principle.
You can have up to 5000 users.
Service account
An IAM user for a service or application.
IAM roles for service accounts provide the ability to manage credentials for your applications, similar to the way that Amazon EC2 instance profiles provide credentials to Amazon EC2 instances. source
Group
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_groups.html
A collection of users with the same permissions.
A way of organizing users and applying permissions to them through a policy.
A user can be a member of zero, one or multiple groups (up to 10 groups maximum). If a user is in multiple groups it gains the permissions of all groups combined together, with any deny taking precedence over any allow. Note that a user may also have permissions applied to its individual user account.
A group can have up to 10 managed policies - see quotas.
Is an IAM identity (see Terms and IAM Identities, thus it can be associated with one or more policies, which determine what actions an identity is authorized to perform, on which AWS resources, and under what conditions.
Is not an entity, thus it cannot be used at the a Principal field of a policy.
You can attach an identity-based policy to a user group so that all of the users in the user group receive the policy's permissions. You cannot identify a user group as a
Principalin a policy (such as a resource-based policy) because groups relate to permissions, not authentication, and principals are authenticated IAM entities. source 1 source 2
Role
A way to delegate permissions without using permanent credentials. Is an IAM identity with permissions assigned. Roles are assumed by users, applications and services (the trusted entities).
When you assume a role you loose any other permissions. Eg if you are an admin but you assume a role, you loose the admin permissions. Thus, the permissions assigned to a role need to include everything required to complete the task.
Roles are a secure way to provide permissions to users and services without using permanent credentials. It’s like a hat: you put a different one for each job, gaining a different set of permissions temporarily to do some action, and when done you leave that role, loosing the extra permissions and going back to the regular permissions of your account. This way you don’t accidentally do something wrong, because you only have the exact permissions required for that task, no more, and for a limited period of time.
- Is an AWS identity with permissions that determine what can and can't do.
- Can be assigned an identity policy for permissions.
- Users, applications and services can assume roles.
- Does not have long term credentials/passwords/access keys. Instead, if a user is assigned a role, access keys are created dynamically and provided to the user temporarily.
- Can be used to delegate access to users, applications or services that don't normally have access to your AWS resources.
- A user who assumes a role temporarily gives up his other own permissions and instead takes on the permissions of the role.
- Eg we can give an EC2 instance a IAM role to temporarily access a S3 bucket using an instance profile.
- Roles remove the need to modify a user's policy each time a change is required.
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/46199680/difference-between-iam-role-and-iam-user-in-aws
We recommend using IAM roles for human users and workloads that access your AWS resources so that they use temporary credentials (instead of IAM users) source
A role is an identity in AWS that doesn't have its own credentials (as a user does) source
Root vs User vs Role
From AWS in Action, page 144.
| Root user | User | Role | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Can have a password to log in to the web console | Must | Yes | No |
| Can have access keys to send requests to the API with the CLI or SDKs | Yes, but not recommended | Yes | No |
| Can belong to a group | No | Yes | No |
| Can be associated with an EC2 instance, Lambda function, ECS container | No | No | Yes |
By default, users and roles can't do anything (except for the root user, which can do everything). You need an identity policy to allow them to perform actions. Users and roles use identity policies.
sts:AssumeRole
To assume a role you use the sts:AssumeRole API action, which returns a set of temporary security credentials (access key ID, a secret access key, and a security token) that you can use to access AWS resources. Is like logging in as the role, and we gain the permissions of the role.
On a trust policy the Action is sts:AssumeRole.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/STS/latest/APIReference/API_AssumeRole.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/reference/sts/assume-role.html
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/63241009/aws-sts-assume-role-in-one-command
EC2 instance profile
Never copy a user’s access keys to an EC2 instance; use IAM roles instead!
Whenever you need to authenticate AWS resources like EC2 instancesI, instead of using an IAM user for authentication, you should use an IAM role. When using an IAM role, your access keys are injected into your EC2 instance automatically.
(AWS in Action p. 148)
A way to attach a role to an EC2 instance, for example to access other services like S3.
If you want to connect to an EC2 instance using Session Manager, you need to attach an instance profile role with the permission policy AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore to the EC2 instance.
In addition to the permission policies, the role needs a trust policy with sts:AssumeRole to allow the EC2 instance to assume the role.
To create an instance profile role do:
- Go to IAM → Roles, and click 'Create role'.
- At the 'Trusted entity type' choose 'AWS service', and at the 'Use case' drop-down list select EC2 (under 'Commonly used services'). This is the trust policy.
- Click 'Next' and select the Permissions policies.
Once the role is created, you can see the trust policy at the role's 'Trust relationship' tab, where the trusted entities is:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "ec2.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
The permissions policy (an inline identity policy) can be anything. For example, if we've given S3 read access with AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess, it will be:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:Get*",
"s3:List*",
"s3:Describe*",
"s3-object-lambda:Get*",
"s3-object-lambda:List*"
],
"Resource": "* "
}
]
}
To attach the role to the EC2 instance, when creating an instance, select the role at the 'IAM instance profile' dropdown. And if the instance is already running, go to the EC2 console → Instances, open the instance, and on the Actions drop-down menu (top right) do Security → Modify IAM role. Select the role and click 'Update IAM role'.
Policy
JSON file. Permissions assigned to a user, group or role.
{
"Sid": "AllowManageOwnSSHPublicKeys", // Who/what is authorized
"Effect": "Allow", // Or "Deny"
"Action": [
// Which task(s) are allowed/denied. It's an API action
"iam:GetSSHPublicKey",
"iam:ListSSHPublicKeys"
],
"Condition": {
// Which condition(s) need to be met for authorization
},
// Resources to which authorized tasks are performed. An ARN or *
"Resource": "arn:aws:iam::*:user/${aws:username}"
}
List of all Actions available for a service: Actions, resources, and condition keys for AWS services
. You need to click on a service.
Not all API operations that are defined by a service can be used as an action in an IAM policy. Some services include permission-only actions that don't directly correspond to an API operation. These actions are indicated with [permission only]. Use this list to determine which actions you can use in an IAM policy.
Also see https://www.awsiamactions.io. (Tip: you can filter by service, by typing for example route53:: https://www.awsiamactions.io/?o=route53%3A)
Console: https://console.aws.amazon.com/iamv2/home?#/policies
Policy Simulator: https://policysim.aws.amazon.com
Policy types - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/access_policies.html#access_policy-types
AWS managed policy:
- About: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/access_policies_managed-vs-inline.html#aws-managed-policies
- List of all AWS managed policies
AWS IAM Policies in a Nutshell - https://start.jcolemorrison.com/aws-iam-policies-in-a-nutshell/
AWS IAM policy linting library - https://github.com/duo-labs/parliament
Policies support versioning to allow changes, see Versioning IAM policies.
EAR
A policy needs to have an EAR to listen what is going to do: Effect, Action and Resource.
Allow and Deny
All permissions are implicitly denied by default. Thus, nothing is allowed unless there's an explicit Allow.
Any explicit Deny overrides any explicit Allows. Thus, if there's multiple policies with conflicting statements, the most restrictive policy is applied.
Note that the root user has full access.
Condition
IAM JSON policy elements: Condition
AWS global condition context keys (available for any action or under unrelated circumstances)
Each service supports different condition keys, see Actions, resources, and condition keys for AWS services
String condition operators: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/reference_policies_elements_condition_operators.html#Conditions_String
StringEquals: Performs exact string matching. Use this when you want to match a specific value with no wildcards.- Example:
"token.actions.githubusercontent.com:sub": "repo:myorg/myrepo:ref:refs/heads/main"only matches that exact branch.
- Example:
StringLike: Allows wildcard matching using*(matches zero or more characters) and?(matches exactly one character).- Example:
"token.actions.githubusercontent.com:sub": "repo:myorg/myrepo:*"matches any branch, tag, or pull request in that repository. - Example:
"token.actions.githubusercontent.com:sub": "repo:myorg/*"matches any repository in that organization.
- Example:
Examples
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/access_policies_examples.html
AdministratorAccess policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "*",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Allows all actions on all resources.
Deny operations to resource if it's not authenticated using MFA
It's called "MFA-protected API access". See Secure API access with MFA.
For an S3 bucket:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Deny",
"Principal": "*",
"Action": "s3:*",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket/*",
"Condition": {
"Null": {
"aws:MultiFactorAuthAge": "true"
}
}
}
]
}
More specific:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Deny",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::238267638199:user/Albert"
},
"Action": [
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:DeleteObject"
],
"Resource": ["arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket", "arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket/*"],
"Condition": {
"Null": {
"aws:MultiFactorAuthAge": "true"
}
}
}
]
}
See more examples of bucket policies requiring MFA: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/userguide/example-bucket-policies.html#example-bucket-policies-MFA
Permissions policy and trust policy (role)
See https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/how-to-use-trust-policies-with-iam-roles/
Trust policy: who
Permissions policy: what
From https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/access_policies.html#policies_resource-based and https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/introduction_access-management.html#intro-access-resource-based-policies:
The IAM service supports only one type of resource-based policy called a role trust policy, which you attach to an IAM role. Because an IAM role is both an identity and a resource that supports resource-based policies, you have to attach both a trust policy and an identity-based policy to an IAM role. Trust policies define which principal entities (accounts, users, roles, and federated users) can assume the role. To learn how IAM roles are different from other resource-based policies, see Cross account resource access in IAM.
Permissions policy
Defines the permissions (Allow or Deny) that the user of the role is able to perform (or is denied from performing), and on which resources. Is an identity-based policy.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "ec2:Describe*",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Trust policy
Who is allowed to assume the role, and under which conditions. Is a resource-based policy.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:root"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
For example, to allow the S3 service to replicate two buckets, we create a Role with this custom trust policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "s3.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
A Lambda function's execution role also needs a trust policy to assume the role.
Identity-based vs resource-based policy
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/access_policies_identity-vs-resource.html
- Identity-based policies apply to users, groups and roles.
- Control what actions the identity can perform, on which resources, and under what conditions.
- Can be further categorized:
- Managed policies.
- AWS managed.
- Customer managed.
- Inline policies. In most cases, we don't recommend using inline policies.
- Managed policies.
- Resource-based policies apply to resources like S3 buckets or DynamoDB tables.
- Control what actions a specified principal can perform on that resource and under what conditions.
- The
Principaldefines who can do the action, and theResourcedefines what resource the action applies to. - Are inline policies.
Example: the AdministratorAccess policy, which can be applied to an administrators group:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "*",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Example: to give a user access to an S3 bucket:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::ACCOUNT_ID:user/MyUser"
},
"Action": "s3:*",
"Resource": ["arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket", "arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket/*"]
}
]
}
Identity-based policy
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/access_policies.html#policies_id-based
Examples: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/access_policies_examples.html
Attached to users, groups and roles (permissions policy). Can be attached in various ways:
- Inline policy: a policy that only applies to single, specific user, group or role. It cannot be reused. If you delete the user, the policy is also deleted.
- An EC2 instance profile role is an inline identity policy. See AWS in Action p. 149.
- Managed policy: either created by you (customer managed) or AWS (AWS managed). Can be reused (standalone, it can be applied to multiple entities). See list of all managed policies.
See Managed policies and inline policies.
With CloudFormation, it’s easy to maintain inline identity policies; that’s why we use inline identity policies most of the time in this book. (AWS in Action p. 147)
Using managed policies can often conflict with following the least-privilege principal. Managed policies usually set the Resource property to *. That’s why we attach our own inline policies to IAM roles or users.
(AWS in Action p. 147)
Does not have a Principal.
You cannot use the
Principalelement in an identity-based policy. Identity-based policies are permissions policies that you attach to IAM identities (users, groups, or roles). In those cases, the principal is implicitly the identity where the policy is attached. source
Example: Allows access to a specific DynamoDB table (source)
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "ListAndDescribe",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"dynamodb:List*",
"dynamodb:DescribeReservedCapacity*",
"dynamodb:DescribeLimits",
"dynamodb:DescribeTimeToLive"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Sid": "SpecificTable",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"dynamodb:BatchGet*",
"dynamodb:DescribeStream",
"dynamodb:DescribeTable",
"dynamodb:Get*",
"dynamodb:Query",
"dynamodb:Scan",
"dynamodb:BatchWrite*",
"dynamodb:CreateTable",
"dynamodb:Delete*",
"dynamodb:Update*",
"dynamodb:PutItem"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:dynamodb:*:*:table/MyTable"
}
]
}
Resource-based policy
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/access_policies.html#policies_resource-based
Attached to a resource like an S3 bucket, a DynamoDB table or a SQS queue. Defines permissions for a principal accessing the resource.
Can be applied to a role too: a trust policy.
Resource-based policies are inline policies. There are no managed resource-based policies. source
If a policy has a Principal, it is a resource policy. The Principal element is unnecessary in an IAM policy because the principal is by default the entity to which the IAM policy attaches. source
On the JSON there's a Principal which defines who gets permission to perform the Action to a specific Resource only.
Not all services support resource-based policies, only a few of them do, see the table at https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/reference_aws-services-that-work-with-iam.html.
Example, an S3 bucket policy (source):
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Id": "BucketPolicy",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllAccess",
"Action": "s3:*",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": "*", // Who is allowed to perform the action
"Resource": ["arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket", "arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket/*"]
}
]
}
Note that when the Action applies to an object, like s3:GetObject, the Resource needs to have /* appended, otherwise the permission applies to the S3 bucket and it doesn't work:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllowPublicAccessToS3Objects",
"Principal": "*",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "s3:GetObject",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::my-static-website-bucket/*" // <- We need '/*' here!
}
]
}
Session policy
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/access_policies.html#policies_session
Limit the permissions of a role when you use the STS AssumeRole action using the CLI or API.
A session policy is a permissions policy which you can optionally pass during an AssumeRole operation. This enables you to place further restrictions on a role's permissions for that session. source
Generate policy based on CloudTrail events
Automatically generates a policy for the permissions that the entity actually used.
Go to IAM → Roles and open a role. At the bottom you have the "Generate policy" button.
It's a recommended best practice
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/access_policies_generate-policy.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/access-analyzer-policy-generation.html
S3 access control policies
Blog post: IAM Policies and Bucket Policies and ACLs! Oh, My! (Controlling Access to S3 Resources) - https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/iam-policies-and-bucket-policies-and-acls-oh-my-controlling-access-to-s3-resources/
There are two ways to control access to S3 buckets using IAM. (There's also ACLs, but should not be used nowadays.)
- IAM Policies
- Identity-based → attached to users, groups and roles
- Does not have
Principal, since thePrincipalis the identity where the policy is attached - Can also be used to grant access to other AWS services in the same policy
- Good for a large number of buckets with varying permissions requirements
- Use it if you prefer to centralize access control in IAM → What can this user do in AWS?
- Size limit of 2048-6144 characters → Use bucket policies if you reach the limit
- Bucket Policies
- Resource-based
- Can only be attached to S3 buckets
- Attached to a specific bucket.
- Similar to an inline policy. If you want to edit it, you'll have to go through every bucket
- Must have a
Principal, which specifies who gets the permissions - Simple way to grant cross-account access without IAM roles
- Use it if you prefer to keep access control policies in S3 → Who can access this S3 bucket?
- Size limit of 20 KB
In both cases, the Resource specifies the bucket.
IAM policy example:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["s3:ListBucket"],
"Resource": ["arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket"]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["s3:GetObject", "s3:DeleteObject"],
"Resource": ["arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket/*"]
}
]
}
Attach the IAM policy to the a user with put-user-policy:
aws iam put-user-policy --user-name MyUser --policy-name S3AccessUserPolicy --policy-document file://iam_policy.json
Bucket policy example:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::ACCOUNT_ID:user/MyUser"
},
"Action": ["s3:PutObject"],
"Resource": ["arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket", "arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket/*"]
}
]
}
Attach the bucket policy to an S3 bucket with put-bucket-policy:
aws s3api put-bucket-policy --bucket my-bucket --policy file://bucket_policy.json
We can restrict access to a specific prefix:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::ACCOUNT_ID:user/MyUser"
},
"Action": "s3:*",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket",
"Condition": {
"StringLike": {
"s3:prefix": "SomeDepartment/*"
}
}
}
]
}
Role vs Policy
https://www.strongdm.com/blog/aws-iam-roles-vs-policies
A role is a type of IAM identity that can be authenticated and authorized to utilize an AWS resource, whereas a policy defines the permissions of the IAM identity.
https://www.learnaws.org/2022/03/03/iam-roles-policies/
An role is very similar to a user, in that it is an identity with permission policies that determine what the identity can and cannot do in AWS. However, a role does not have any credentials (password or access keys) associated with it. Policies determine what actions a user, role, or member of a user group can perform, on which AWS resources, and under what conditions.
You attach IAM policies (which contain a set of permissions) to an IAM Role. Therefore, a single IAM roles can have multiple IAM policies in it. Lastly, a user can "assume" an IAM Role, meaning it will inherit automatically the policy or policies attached to that Role.
Principal
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/reference_policies_elements_principal.html
A Principal is a user, account, service, or other entity that is allowed or denied access to a resource source
It can be a (source):
- AWS account and root user
- IAM role
- Role session (assume role)
- IAM user
- Federated user session (Google, Facebook etc)
- AWS service (ie an application)
Note that a Group is not a principal since:
You cannot identify a user group as a principal in a policy (such as a resource-based policy) because groups relate to permissions, not authentication, and principals are authenticated IAM entities source
Cross-account access
Cross account resource access in IAM
You can attach a resource policy directly to the resource that you want to share, or use a role as a proxy.
When using a role, the identity who assumes the role gets temporary credentials, and gives up their original permissions. That's not the case with resource-based policies: the principal will have access to resources in its own account and the other account at the same time. This can be useful if we need to copy information from one account to another, for example. Another difference is that the role can be used in the management console (we can switch to it), but the resource policy can only be used programmatically.
In cross account access, a principal needs an Allow in the identity policy and the resource-based policy. See Resource-based policies to delegate AWS permissions.
IAM tutorial: Delegate access across AWS accounts using IAM roles
Access for an IAM user in another AWS account that you own. Uses a role.
Access to AWS accounts owned by third parties → Grant access to an account that you do not own or control
From https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/access_policies.html#policies_resource-based
To enable cross-account access, you can specify an entire account or IAM entities in another account as the principal in a resource-based policy. Adding a cross-account principal to a resource-based policy is only half of establishing the trust relationship. When the principal and the resource are in separate AWS accounts, you must also use an identity-based policy to grant the principal access to the resource. However, if a resource-based policy grants access to a principal in the same account, no additional identity-based policy is required.
https://repost.aws/knowledge-center/cross-account-access-iam - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0Wo5pH5zibk
Examples in SQS: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSSimpleQueueService/latest/SQSDeveloperGuide/sqs-basic-examples-of-sqs-policies.html
Examples in S3:
- Example 2: Bucket owner granting cross-account bucket permissions → Uses a bucket policy instead of a role
- Example 4: Bucket owner granting cross-account permission to objects it does not own
Example: allow another account to send messages to an SQS queue using a resource policy
Use a resource-based policy attached to an SQS queue in account 444455556666 that grants another AWS account (111122223333) the sqs:SendMessage action.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": ["111122223333"]
},
"Action": "sqs:SendMessage",
"Resource": "arn:aws:sqs:us-east-1:444455556666:MyQueue"
}
]
}
Even though account 444455556666 has granted cross-account access to the queue via the resource policy, an IAM user or role in account 111122223333 must still have an IAM policy that explicitly allows it to perform actions on the queue:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "sqs:SendMessage",
"Resource": "arn:aws:sqs:us-east-1:444455556666:MyQueue"
}
]
}
Example: get access to an S3 bucket in another account by assuming a role
From https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nealdct/aws-saa-code/refs/heads/main/aws-iam/cross-account-role.md and Access for an IAM user in another AWS account that you own.
Account A has a private S3 bucket and a role. A user in account B gains access to the bucket by assuming the role.
Role trust policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "account-B-id"
},
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"sts:ExternalId": "some-password"
}
}
}
]
}
Role permissions policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllowBucketAccess",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["s3:GetObject", "s3:PutObject", "s3:ListBucket"],
"Resource": ["arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket", "arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket/*"]
}
]
}
To assume the role, a user in account B must have permission to call the Security Token Service AssumeRole action for the role.
To assume the role, a user in account B can click "Switch Role" in the console or run:
aws sts assume-role --role-arn arn:aws:iam::<account-a-id>:role/<role-name> --role-session-name mysession --external-id some-password
This call returns temporary credentials: an Access Key ID, Secret Access Key and Session Token.
Regarding the optional external ID, when creating the role at the console it says:
You can increase the security of your role by requiring an optional external identifier, which prevents "confused deputy" attacks. This is recommended if you do not own or have administrative access to the account that can assume this role. The external ID can include any characters that you choose. To assume this role, users must be in the trusted account and provide this exact external ID.
For more information on when to use external IDs, see Access to AWS accounts owned by third parties.
Avoid access keys if possible
As a best practice, use temporary security credentials (such as IAM roles) instead of creating long-term credentials like access keys. source
In many scenarios, you don't need long-term access keys that never expire (as you have when you create access keys for an IAM user). Instead, you can create IAM roles and generate temporary security credentials. Temporary security credentials include an access key ID and a secret access key, but they also include a security token that indicates when the credentials expire. After they expire, they're no longer valid. source
Access keys have the permissions of the IAM user that created them. If compromised, is like getting access to the IAM user account, like having your username and password. They are long term credentials; you need to review them when an employee leaves your company.
In contrast, IAM roles are assumed using short-term credentials generated by the Security Token Service. The credentials are renewed continuously and automatically if required, for example in EC2 instance profiles (from Retrieve security credentials from instance metadata):
These security credentials are temporary and we rotate them automatically. We make new credentials available at least five minutes before the expiration of the old credentials.
See Alternatives to long-term access keys
- Don't embed long-term access keys and secret access keys in your application code or in a code repository
- Use IAM roles to generate temporary security credentials whenever possible
- Use alternatives to long-term access keys for the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) or the
aws-shell- AWS CloudShell
- AWS CLI Version 2 integration with AWS IAM Identity Center docs
- Don't create long-term access keys for human users who need access to applications or AWS services
- Don't store long-term access keys within an AWS compute service
Note that there are cases in which you can't use IAM roles to provide temporary credentials, such as for WordPress plugins. See Update access keys when needed for use cases that require long-term credentials.
A company with several departments that manage AWS
- Create an IAM group for each department.
- Create a policy and assign it to the group.
- Create IAM users for each person on each department and add them to their respective groups.
Finding your AWS account ID
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/console_account-alias.html#FindingYourAWSId
aws sts get-caller-identity
aws sts get-caller-identity --query Account --output text
Multi-factor authentication
Supported MFA methods/devices - https://aws.amazon.com/iam/features/mfa/
Using multi-factor authentication (MFA) in AWS - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_credentials_mfa.html
Add MFA to other users
When you are logged as root, follow this steps to assign an MFA device to an IAM user like the Administrator. This works for yourself too if you are not the root user (the root user doesn't appear at the IAM users list).
Go to the IAM Dashboard → Users and select a user. Click the 'Security credentials' tab and do 'Assign MFA device'. If you are using 1password to generate OTP codes then set:
- MFA device name: 1password
- MFA device: Authenticator app
Enforce MFA to users
Prevent users to perform actions unless they've set up MFA with a policy - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cP_IbgnK8yk - https://github.com/iaasacademy/aws-how-to-guide/tree/main/Enable%20IAM%20Users%20to%20setup%20MFA - https://iaasacademy.com/aws-how-to-guides/enable-iam-users-to-manage-their-mfa-settings-aws-how-to-guide/
Perform API call operations protected by MFA
Use sts get-session-token to get temporary credentials to access a service protected with MFA from the CLI:
aws sts get-session-token --serial-number arn:aws:iam::ACCOUNT_ID:mfa/DEVICE_NAME --token-code <otp-token>
Returns an AccessKeyId, SecretAccessKey and SessionToken.
Documentation:
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/reference/sts/get-session-token.html
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/STS/latest/APIReference/API_GetSessionToken.html
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_credentials_temp_request.html#api_getsessiontoken
Create the first IAM admin user
We recommend that you not use the root level credentials for anything other than initial setup of the account and the creation of the IAM user account with administrator permissions attached via policy source
There are 2 guides/tutorials that explain how to set up the admin user:
- Tutorial: Secure Your AWS Account - https://aws.amazon.com/getting-started/guides/setup-environment/module-two/
- Creating your first IAM admin user and user group - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/getting-started_create-admin-group.html → This is the tutorial I've followed, see the steps above
Steps
TLDR: create a group 'Administrators' with the AdministratorAccess policy, then create a user and add it to the group.
- Sign in to the console as Root user.
- Click your name at the top navbar → Account. At the section 'IAM User and Role Access to Billing Information' click 'Edit' and enable 'Activate IAM Access'.
- Go to the IAM console → Users and click 'Create user'.
- On the 'Set user details' page do:
- Set 'User name' to 'Administrator' or similar (eg 'BootcampAdmin').
- Check 'Provide user access to the AWS Management Console'.
- Select 'I want to create an IAM user'.
- Set a password at 'Custom password' and save it.
- Uncheck 'Users must create a new password at next sign-in'.
- Click 'Next'.
- On the 'Set permissions' page do:
- Click 'Add user to group' and then 'Create group'.
- Set 'Group name' to 'Administrators'.
- Check the policy
AdministratorAccess. - Click 'Create user group'.
- At the 'User groups' list, check the newly created group 'Administrators' to add the user to the group.
- Click 'Next'.
- Click 'Add user to group' and then 'Create group'.
- On the 'Review and create' page optionally add tags.
- Click 'Create user'.
Don't forget to enable MFA for the admin user. Since you are logged as root now, follow this steps.
Using the CLI
aws iam create-group --group-name Administrators
aws iam attach-group-policy --group-name Administrators --policy-arn "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AdministratorAccess"
aws iam create-user --user-name MyUser
aws iam add-user-to-group --group-name Administrators --user-name MyUser
aws iam create-login-profile --user-name MyUser --password 'XB5j8stK4YVW3b'
Password policy
Set an account password policy for IAM users - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_credentials_passwords_account-policy.html
Go to IAM → Account settings and on the Password policy box click the 'Edit' button.
https://www.netskope.com/blog/a-real-world-look-at-aws-best-practices-password-policies
ARN
Use https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=<arn> to navigate to the AWS console page of the resource. There are more links supported, see https://wut.dev/blog/2025/06/21/hidden-aws-console-go-urls.html.
If you use Firefox, you can create a bookmark with a URL https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=%s and a keyword arn. Then you can type arn arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket at the address bar and it navigates to the S3 bucket page.
You can also use https://link2aws.github.io. It can be used to redirect to the AWS console by appending the ARN with #<arn>, for example: https://link2aws.github.io/#arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket
Sources: Tweet, StackOverflow, CLI script
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/reference-arns.html
A unique identifier of a resource.
List of possible resource type ARNs that you can specify as a Resource in a resource policy: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/service-authorization/latest/reference/reference_policies_actions-resources-contextkeys.html
Format:
arn:partition:service:region:account-id:resource-id
arn:partition:service:region:account-id:resource-type/resource-id
arn:partition:service:region:account-id:resource-type:resource-id
Examples:
# IAM user
arn:aws:iam::123456789012:user/johndoe
# VPC
arn:aws:ec2:us-east-1:123456789012:vpc/vpc-0e9801d129EXAMPLE
# EC2 instance
arn:aws:ec2:us-east-1:123456789012:instance/i-0e9801d129f56c97
CLI
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/reference/iam/
Examples - https://github.com/aws/aws-cli/tree/develop/awscli/examples/iam
User
aws iam create-user --user-name MyUser
You should enable MFA for the user after creating it. See Add MFA to other users.
Set a password so that the user can login to the web management console docs
aws iam create-login-profile --user-name MyUser --password 'XB5j8stK4YVW3b'
aws iam list-users
Create access keys for a user to allow access using the CLI or SDKs:
aws iam create-access-key --user-name MyUser
Copy the AccessKeyId and SecretAccessKey from the output and run aws configure --profile MyUser to set up the CLI for the user.
Group
aws iam create-group --group-name Administrators
Attach a Policy to a group docs
aws iam attach-group-policy --group-name Administrators --policy-arn "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AdministratorAccess"
Add user to group docs
aws iam add-user-to-group --group-name Administrators --user-name MyUser
Role
aws iam get-role --role-name <role-name>
aws iam get-role --role-name <role-name> | \
jq -r '.Role.AssumeRolePolicyDocument.Statement[].Action[]'
Get inline permissions policies attached to a role docs:
aws iam list-role-policies --role-name <role-name>
Get managed permissions policies attached to a role docs:
aws iam list-attached-role-policies --role-name <role-name>
aws iam list-attached-role-policies --role-name <role-name> | \
jq -r '.AttachedPolicies[].PolicyName'
aws iam create-role --role-name <role-name> --assume-role-policy-document file://trust-policy.json --output text --query 'Role.Arn'
Example of trust policy document:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::111222333444:user/Albert"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
Attach or update an inline permissions policy to a role docs
aws iam put-role-policy --role-name <role-name> --policy-name <policy-name> --policy-document file://permissions-policy.json
Example of permissions policy document:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["eks:Describe*", "ssm:GetParameters"],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Attach an AWS managed policy to a role docs
aws iam attach-role-policy \
--role-name MyAmazonEKSClusterRole \
--policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKSClusterPolicy
Attach an inline policy to a user docs
aws iam put-user-policy --user-name MyUser --policy-name MyUserPolicy --policy-document file://iam-user-policy.json
Example of inline policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["s3:ListBucket"],
"Resource": ["arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket"]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["s3:GetObject", "s3:DeleteObject"],
"Resource": ["arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket/*"]
}
]
}
Change the trust policy of a role docs
aws iam update-assume-role-policy --role-name <role-name> --policy-document file://new-trust-policy.json
aws iam update-assume-role-policy --role-name <role-name> --policy-document '{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "eks.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": [
"sts:AssumeRole",
"sts:TagSession"
]
}
]
}'
Delete role:
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_roles_manage_delete.html
- First remove the role from instance profile:
aws iam remove-role-from-instance-profile --instance-profile-name <instance-profile-name> --role-name <role-name> - If there's a policy attached to the role, remove it:
aws iam delete-role-policy --role-name <role-name> --policy-name <policy-name> - Finally, remove the role:
aws iam delete-role --role-name <role-name> - If you get the error "Cannot delete entity, must remove roles from instance profile first" on the console when trying to delete a role, use the CLI instead.
Policy
aws iam create-policy --policy-name MyPolicy --policy-document file://my-policy.json
Get the ARN of a policy by name:
aws iam list-policies --query 'Policies[?PolicyName==`AdministratorAccess`].{ARN:Arn}' --output text
# arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AdministratorAccess
POLICY_ARN=$(aws iam list-policies --query 'Policies[?PolicyName==`AdministratorAccess`].{ARN:Arn}' --output text)
Permissions boundaries
Sets the maximum permissions that an identity-based policy can grant to an IAM entity. Is an IAM policy. Can be applied to users and roles. Used to restrict permissions in order to prevent privilege escalation.
Important: permissions boundaries don't grant permissions, they control the permissions you have. You still need to have the permissions granted to you through a role for example.
When a developer has permissions to create IAM users and roles, it can create a user or role with excessive permissions. To prevent privilege escalation, we can add a condition to a developer's IAM policy that allows the developer to create a role only if a permissions boundary is attached to the role.
(Documentation) Permissions boundaries for IAM entities - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/access_policies_boundaries.html
When and where to use IAM permissions boundaries - https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/when-and-where-to-use-iam-permissions-boundaries/
The predominant use case for permissions boundaries is to limit privileges available to IAM roles created by developers (referred to as delegated administrators in the IAM documentation) who have permissions to create and manage these roles.
How can I use permissions boundaries to limit the scope of IAM users and roles, and also prevent privilege escalation? - https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/iam-permission-boundaries/
How can I resolve access denied issues caused by permissions boundaries? - https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/iam-access-denied-permissions-boundary/
Prevent privilege escalation with AWS IAM permission boundaries - https://iaasacademy.com/aws-how-to-guides/aws-iam-permissions-boundaries-help-to-prevent-privilege-escalations - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LZdfxS2DnFw
AWS Permission Boundaries for Dummies - https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=33192295
It's a best practice - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/best-practices.html#bp-permissions-boundaries
Example - https://github.com/aws-samples/example-permissions-boundary
Security Token Service (STS)
Provides temporary, short lived credentials to be used with identity federation, delegation, cross-account access, and IAM roles.
CLI Reference - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/reference/sts/
API Reference - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/STS/latest/APIReference/welcome.html
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/63241009/aws-sts-assume-role-in-one-command
Temporary security credentials in IAM - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_credentials_temp.html
Session policy - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/access_policies.html#policies_session
Eventually consistent
From https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/introduction.html
IAM, like many other AWS services, is eventually consistent. IAM achieves high availability by replicating data across multiple servers within Amazon's data centers around the world. If a request to change some data is successful, the change is committed and safely stored. However, the change must be replicated across IAM, which can take some time.
Changes that I make are not always immediately visible - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/troubleshoot_general.html#troubleshoot_general_eventual-consistency
www.it-automation.com/2021/06/06/how-to-deal-with-eventual-consistency-in-AWS-IAM.html